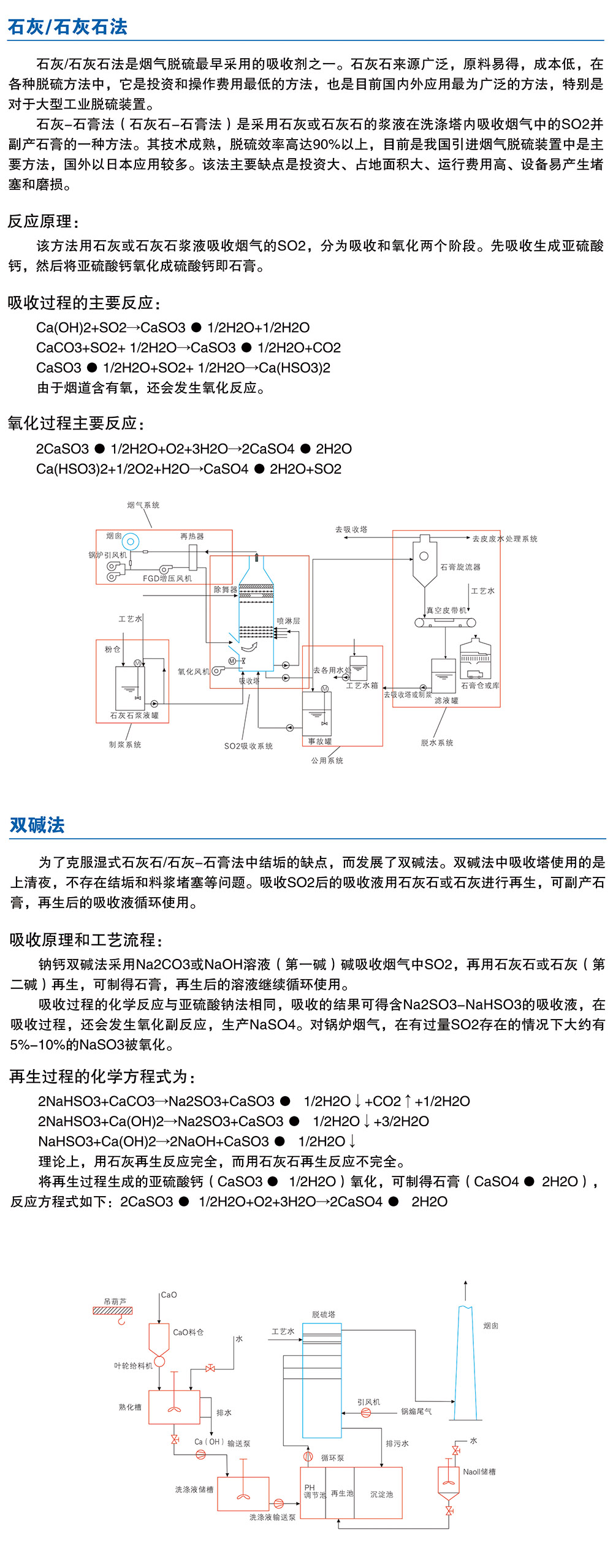
The wet FGD process belongs to the desulfurization technology after coal combustion. After the whole desulfurization system is located in the air preheater and the precipitator, the desulfurization process is carried out in a liquid state, the desulfurizer and the desulfurization product are all in a wet state, and the reaction temperature of the desulfurization process is lower than the dew point, so the flue gas after desulfurization generally needs further Heating is discharged from the chimney. Wet flue gas desulfurization is a gaseous reaction. It has the advantages of fast desulfurization reaction, high desulfurization efficiency and high utilization rate of absorbent, simple and reliable process, low operating cost and good performance. It is suitable for desulfurization of boilers in thermal power plants. At present, domestic thermal power plants use more than 85% of the wet FGD process.
The absorbent for wet flue gas desulfurization is mainly limestone and lime. The main component of limestone is CaCO3. The main component of lime is CaO, which is called limestone and lime/gypsum. There is also a widely used nano calcium double base method, and the absorbent is NaOH/CaO. The absorbent of the calcium magnesium method is MgO/CaO. The magnesium absorbent is Mg(OH)2.
The working process of the wet flue gas desulfurization (FGD) process system is: the flue gas from the outlet of the boiler induced draft fan is boosted by the FGD system (BoosterUP Fan, BUF for short) Raise the indenter and enter the Gas Gas Heater (GGH) to cool down. The high temperature raw flue gas enters the absorption tower after cooling. After passing through the absorption tower, the SO2 in the flue gas is absorbed by the spray slurry while the flue gas is cooled in the absorption tower. The absorption tower circulation pump continuously sends the slurry from the reaction tank to one or more spray mother tubes inserted into the absorption tower, and each of the mother tubes has a plurality of branch pipes, and the branch pipes are provided with a large number of independent mists. The nozzle is atomized and sprayed into small droplets by a nozzle. Below the absorption tower body is a reaction tank, which is integrated into one. The reaction tank is both a container for collecting the spray slurry and a base for the tower body. The washed flue gas is passed through a mist eliminator (Mist Eliminator, ME for short) to remove the slurry droplets entrained in the flue gas before leaving the absorption tower system. After leaving the demister (ME), the clean saturated flue gas is heated back to the gas-gas heater (GGH) to raise the flue gas, and then exits the flue through the FGD system and is discharged into the atmosphere by the chimney.
The wet flue gas desulfurization FGD process usually includes milling, slurry preparation, pre-absorption, absorption tower, oxidation, and flue gas heat transfer. Subsystems such as gypsum dehydration and other auxiliary systems. There are also differences in the process and arrangement of different desulfurization technologies. However, regardless of the wet flue gas desulfurization technology, the basic process system includes: slurry preparation system, accident slurry discharge system, electrical appliance and detection control system.